Subtopic 5.1: DNA Methylation Assay
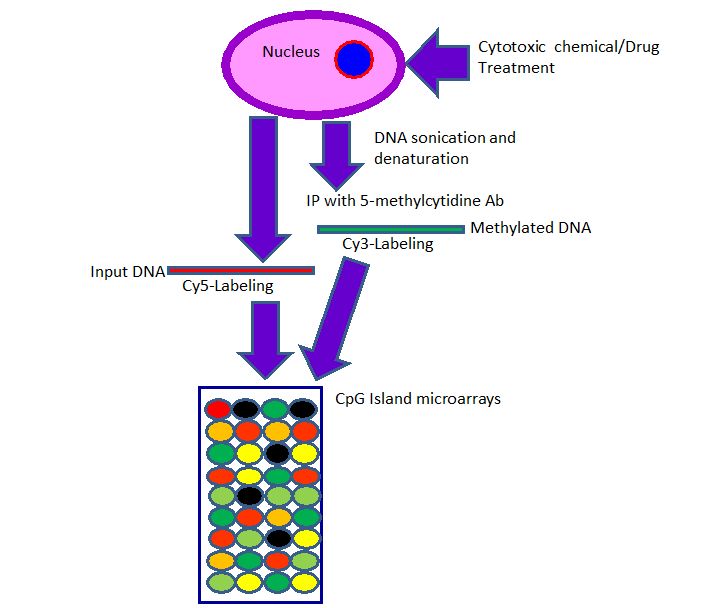
DNA methylation assays are important to know the epigenetic modification which is a heritable, enzyme-induced modification without alteration the nucleotide base pairs. The transfer of a methyl-group to the 5-carbon on the cytosine in a CpG dinucleotide happens in the DNA methylation by DNA methyltransferases (DNMT1, DNMT3A, and DNMT3B). The high level of promoter CpG island methylation results in gene silencing. The methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP)-chip technique is used for DNA methylation assay.
In brief, the MeDIP-chip procedure is mentioned as follows. The genomic DNA is sheared to low molecular weight fragments (approximately 400 bp) by sonication. Then, the methylated DNAs are immunoprecipitated with the anti-methyl-cytosine antibody, and are amplified with PCR, if source material is less. Input and methylated DNA are labeled with fluorescent dyes Cy3 (green) and Cy5 (red), pooled, denatured, and are hybridized to a microarray slide containing all the annotated human CpG islands or other whole genome or promoter microarray designs. Then the slide is scanned using a scanner and each image is analyzed with the image analysis software ( Figure 1).
In brief, the MeDIP-chip procedure is mentioned as follows. The genomic DNA is sheared to low molecular weight fragments (approximately 400 bp) by sonication. Then, the methylated DNAs are immunoprecipitated with the anti-methyl-cytosine antibody, and are amplified with PCR, if source material is less. Input and methylated DNA are labeled with fluorescent dyes Cy3 (green) and Cy5 (red), pooled, denatured, and are hybridized to a microarray slide containing all the annotated human CpG islands or other whole genome or promoter microarray designs. Then the slide is scanned using a scanner and each image is analyzed with the image analysis software ( Figure 1).