Subtopic 2.2: Macro Lesions (Chromosomal Mutation)
- Macro lesions are chromosomal mutations with mutagens and are with distinct morphological changes in the phenotype.
- These morphological changes of chromosomes can be cytologically visible under microscope.
- Macro lesions are following types:
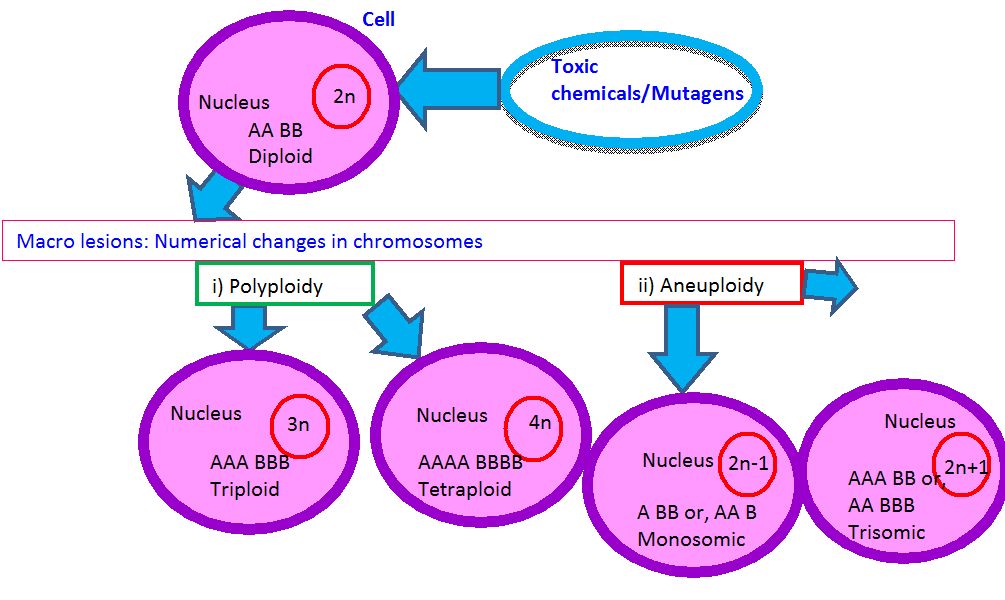
2.2a. Numerical changes in chromosomes (Figure 2):
i) Polyploidy: Duplication of entire set of chromosome to triploid or tetraploid.
ii) Aneuploidy: Changes of single missing chromosome to monosomy or three copies of a single chromosome to trisomy.
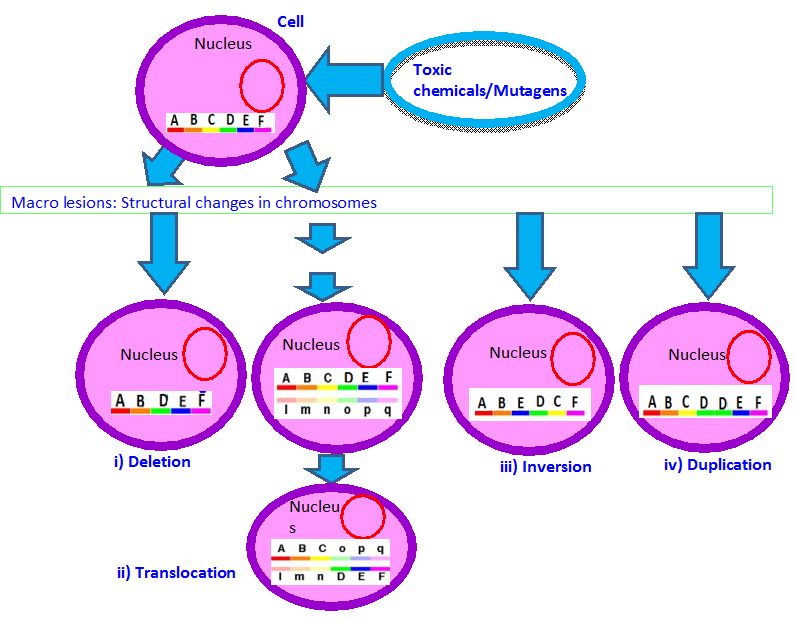
2.2b. Structural changes in chromosomes (Figure 3):
i) Deletion: loss of chromosome segment
ii) Translocation:
A segment of one chromosome becomes attached to a non homologous chromosome.
It can be one way transfer as simple translocation and two way transfer as reciprocal translocation.
iii) Inversion: A change in the direction of material along a single chromosome.
iv) Duplication: Repetition of chromosome segment
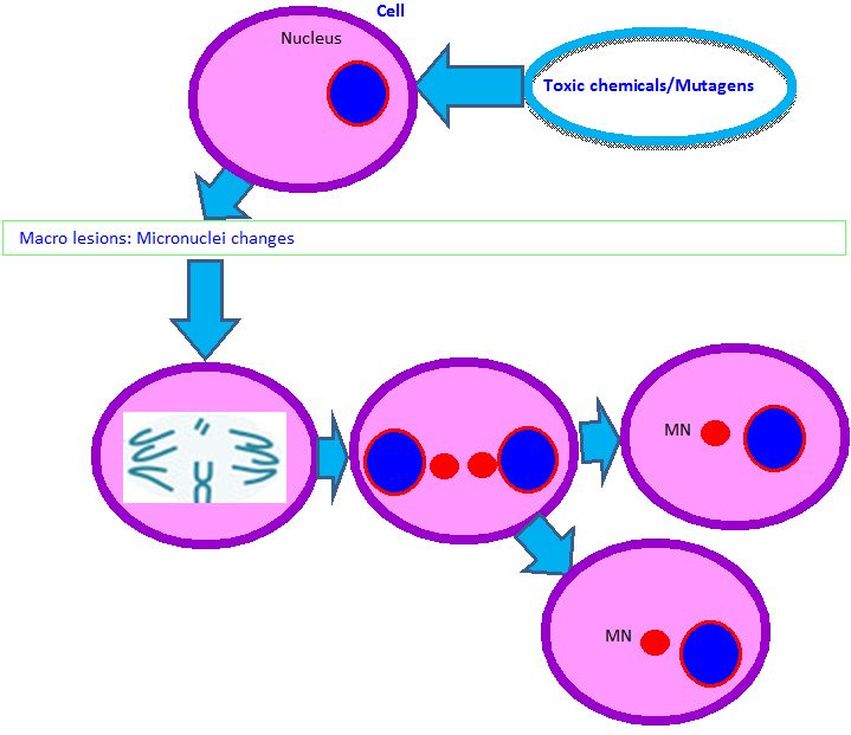
2.2c. Micronuclei changes (Figure 4):
- Micronuclei (MN) are the damaged chromosome fragments or whole chromosomes that were not incorporated into the cell nucleus and stayed as the extra-nuclear bodies after the cell division.
- MN can be resulted by the defects of the cell repair machinery and by the accumulation of damaged DNA and chromosomal aberrations.