NOAEL and LOAEL
Results from research studies establish the highest doses at which no toxic effects were identified and the lowest doses at which toxic or adverse effects were observed. The terms often used to describe these outcomes are:
These terms refer to the actual doses used in human clinical or experimental animal studies. They are defined as follows:
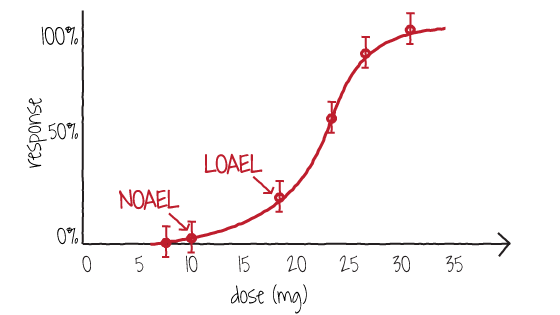
Figure 1 shows a dose-response curve where the NOAEL occurs at 10 mg and the LOAEL occurs at 18 mg.
Results from research studies establish the highest doses at which no toxic effects were identified and the lowest doses at which toxic or adverse effects were observed. The terms often used to describe these outcomes are:
- No Observed Adverse Effect Level (NOAEL)
- Lowest Observed Adverse Effect Level (LOAEL)
These terms refer to the actual doses used in human clinical or experimental animal studies. They are defined as follows:
- NOAEL -- Highest dose at which there was not an observed toxic or adverse effect.
- LOAEL -- Lowest dose at which there was an observed toxic or adverse effect.
Figure 1 shows a dose-response curve where the NOAEL occurs at 10 mg and the LOAEL occurs at 18 mg.
Figure 1. A dose-response curve showing doses where the NOAEL and LOAEL occur for a substance
(Image Source: NLM)
(Image Source: NLM)
Sometimes the terms No Observed Effect Level (NOEL) and Lowest Observed Effect Level (LOEL) are also used. NOELs and LOELs do not necessarily imply toxic or harmful effects and can be used to describe beneficial effects of substances.
The NOAEL, LOAEL, NOEL, and LOEL are commonly used in risk assessments and research. For example, this U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) publication for industry describes a process for estimating the maximum safe starting dose of drugs tested in clinical trials. It provides extensive information about these concepts and their utility when developing new drugs.
NOAELs and LOAELs are also included in the Noncarcinogenic Risk Assessment section where they are applied using the benchmark dose (BMD) method.
The NOAEL, LOAEL, NOEL, and LOEL are commonly used in risk assessments and research. For example, this U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) publication for industry describes a process for estimating the maximum safe starting dose of drugs tested in clinical trials. It provides extensive information about these concepts and their utility when developing new drugs.
NOAELs and LOAELs are also included in the Noncarcinogenic Risk Assessment section where they are applied using the benchmark dose (BMD) method.
Knowledge Check (Solutions on next page)
1) Which of the following is not one of the Three Rs of estimating acute toxicity?
a) Replace animals in science by in vitro, in silico, and other approaches
b) Reduce the number of animals used
c) Refine care and procedures to minimize pain and distress
d) Randomize the selected test animals
2) The Therapeutic Index (TI) is used to:
a) Compare the therapeutically effective dose to the toxic dose of a pharmaceutical agent
b) Calculate the lethal dose level for different pharmaceuticals
c) Compare the lethal dose to the therapeutically effective dose of a pharmaceutical agent
3)The Margin of Safety (MOS) of a drug is the:
a) Amount of a pharmaceutical that can be given before toxicity first appears
b) Difference between the Effective Dose to 50% of the population (ED50) and the Toxic Dose to 50% of the population (TD50)
c) Ratio of the Toxic Dose to 1% of the population (TD01) to the Effective Dose to 99% of the population (ED99)
4) The No Observed Adverse Effect Level (NOAEL) is the:
a) Lowest dose at which there was no observed toxic or adverse affect
b) Highest dose at which there was no observed toxic or adverse effect
c) Highest dose at which there was an observed adverse effect
5) The Lowest Observed Adverse Effect Level (LOAEL) is the:
a) Lowest dose at which there was an observed toxic or adverse effect
b) Lowest dose at which there was no observed toxic or adverse effect
c) Highest dose at which there was an observed adverse effect
1) Which of the following is not one of the Three Rs of estimating acute toxicity?
a) Replace animals in science by in vitro, in silico, and other approaches
b) Reduce the number of animals used
c) Refine care and procedures to minimize pain and distress
d) Randomize the selected test animals
2) The Therapeutic Index (TI) is used to:
a) Compare the therapeutically effective dose to the toxic dose of a pharmaceutical agent
b) Calculate the lethal dose level for different pharmaceuticals
c) Compare the lethal dose to the therapeutically effective dose of a pharmaceutical agent
3)The Margin of Safety (MOS) of a drug is the:
a) Amount of a pharmaceutical that can be given before toxicity first appears
b) Difference between the Effective Dose to 50% of the population (ED50) and the Toxic Dose to 50% of the population (TD50)
c) Ratio of the Toxic Dose to 1% of the population (TD01) to the Effective Dose to 99% of the population (ED99)
4) The No Observed Adverse Effect Level (NOAEL) is the:
a) Lowest dose at which there was no observed toxic or adverse affect
b) Highest dose at which there was no observed toxic or adverse effect
c) Highest dose at which there was an observed adverse effect
5) The Lowest Observed Adverse Effect Level (LOAEL) is the:
a) Lowest dose at which there was an observed toxic or adverse effect
b) Lowest dose at which there was no observed toxic or adverse effect
c) Highest dose at which there was an observed adverse effect