Subtopic 4.4: microRNAs
miRNAs have an important role in gene regulation and they can influence biological functions including cell differentiation and proliferation during normal development and pathological responses.
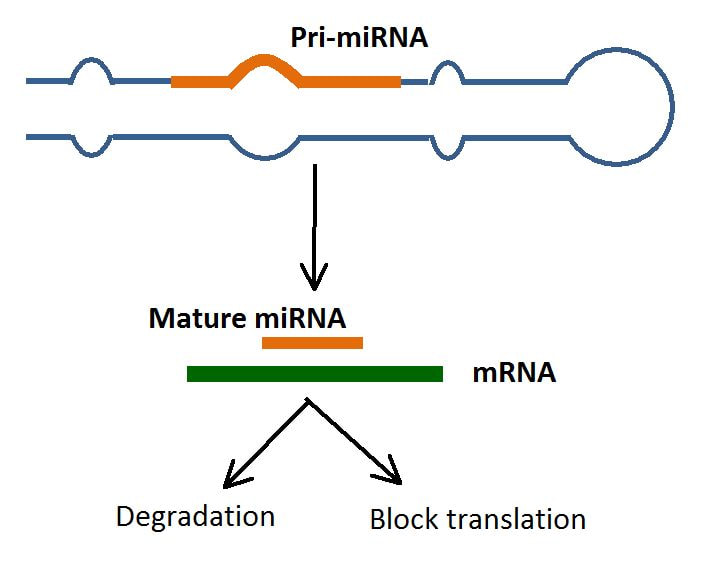
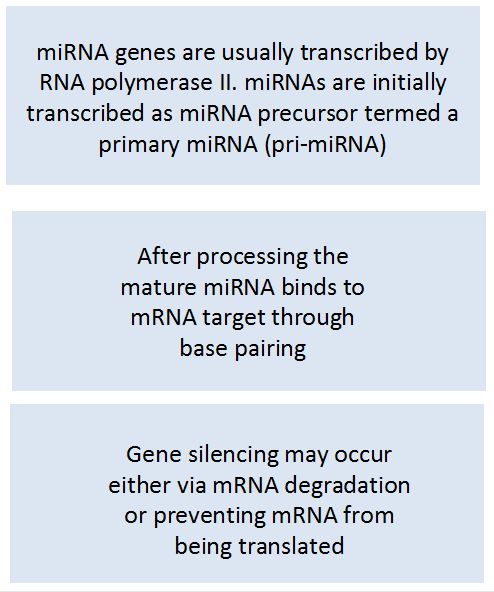
miRNAs are small non-coding RNA molecules (containing about 22 nucleotides), derived from regions of RNA transcripts that fold back on themselves to form short hairpins.
miRNAs regulate gene expression at the post transcriptional level.
A number of miRNAs may bind to specific regions of the messenger RNA (mRNA) and block its translation to proteins.
Alteration of the expression of miRNAs is believed to contribute to the progression of tumorigenesis and other diseases.