Subtopic 2.4: Cell Signaling
Cell signaling consists in the ability of cells to respond to environment changes through signals received outside their borders. Cells may receive many signals simultaneously and also send out messages to other cells.
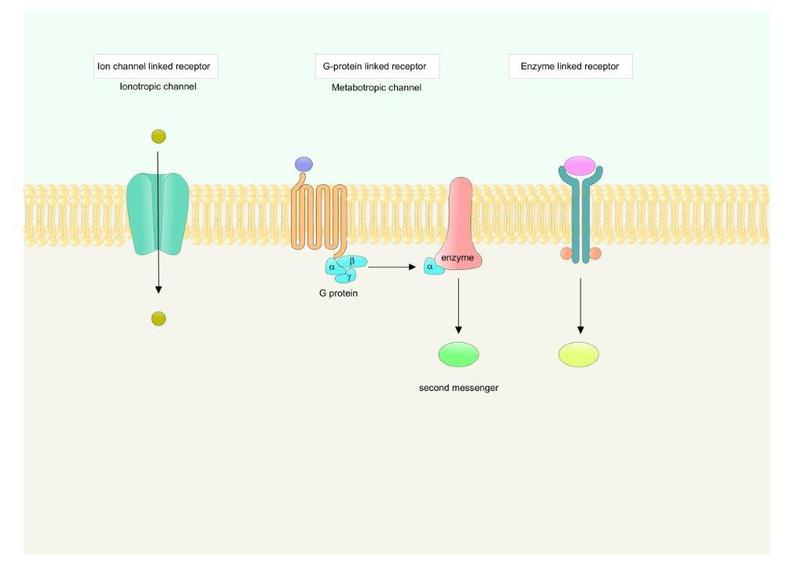
Cells have proteins called receptors, that are generally transmembrane proteins, which bind to signaling molecules outside the cell and subsequently transmit the signal through a sequence of molecular switches to internal signaling pathways and initiate a physiological response. Different receptors are specific for different molecules. In fact, there are hundreds of receptor types found in cells, and varying cell types have different populations of receptors.
Examples of receptors membrane:
- G-protein-coupled receptors
- Ion channel receptors
- Enzyme-linked receptors
Receptor may be located in the cellular membrane (important to receive extracellular signals) but also may be present inside the cell or inside the nucleus.