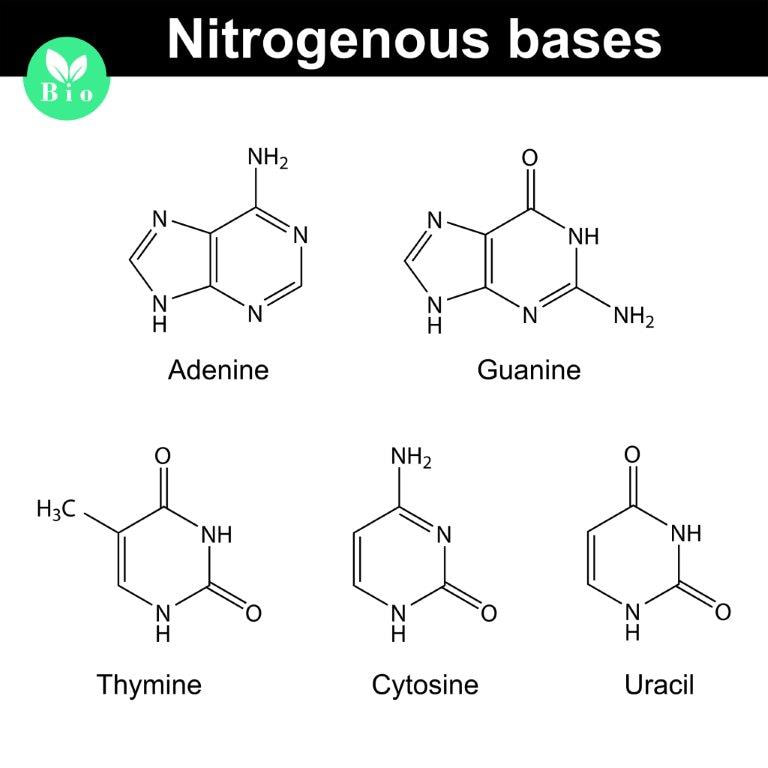
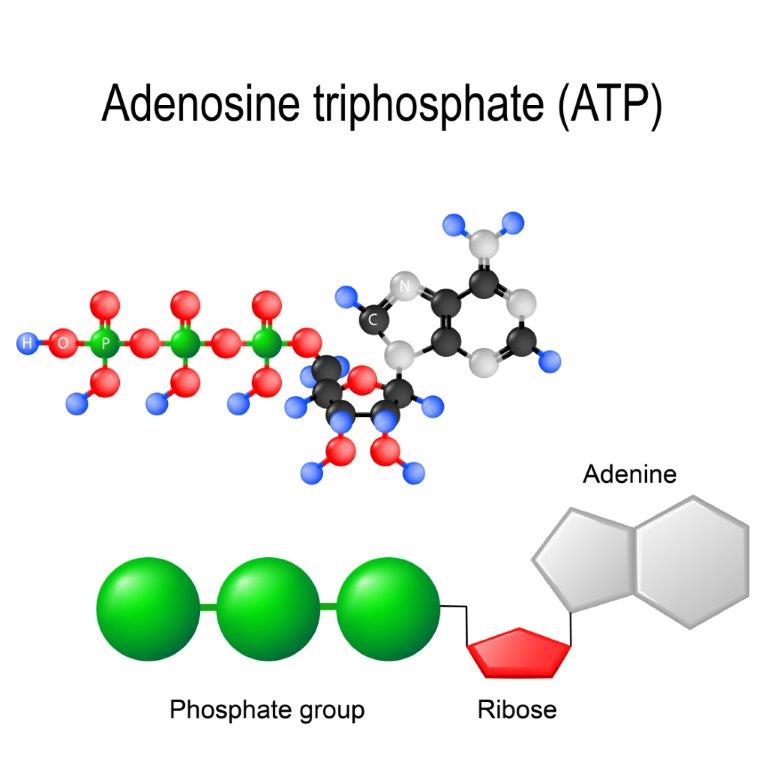
Subtopic 1.4: Nucleosides and nucleotides
Nucleosides and nucleotides are involved in the preservation and transmission of the genetic information of all living creatures. In addition, they play roles in biological energy storage and transmission, signaling and regulation of various aspects of metabolism.
|
The unique structure and interaction of these molecules serve as the fundamental building block of RNA and DNA molecules and allow fundamental processes of DNA replication and protein synthesis to occur. Components of Nucleotides:
|