Topic 5: State Regulatory Toxicology
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
After completing this lesson, you will be able to:
After completing this lesson, you will be able to:
- Define what is meant by “State Regulatory Toxicology”.
- Give an example of a state regulatory regulation.
What is State Regulatory Toxicology?
- Deals with regulatory toxicology for the US on a state level (e.g. Texas, Delaware, Arizona).
- Established by authorities applicable to a given state.
- State regulatory toxicology only applies with the state’s boundaries; however, they may influence adjacent states or even national regulatory toxicology.
- Under the layer of the US national government sits a complex web of state and local laws and policies, in addition to regulatory authorities.
- The make-up of state and local governments varies widely across the US; while they have mutual specific features, their organizations differ.
- Whatever their design, state and local governments can sometimes have a much greater impact on people's lives than the federal government.
The Federal-State Toxicology and Risk Analysis Committee (FSTRAC) is made up of representatives from U.S. state health and environmental agencies and U.S. EPA personnel.
- Is an integral part of EPA’s communication strategy with states and tribes for human health risks associated with water contamination.
- Fosters cooperation, consistency, and an understanding of EPA’s and different states’ goals and problems in human health risk assessment.
- Allows states and the federal government to work together on issues related to the development and implementation of regulations and criteria under the Safe Drinking Water Act and Clean Water Act.
FSTRAC members have supported development of:
- Human Health Benchmarks for Pesticides (HHBP)
-Used to help assess drinking water quality for pesticides that do not have other regulatory toxicology standards .
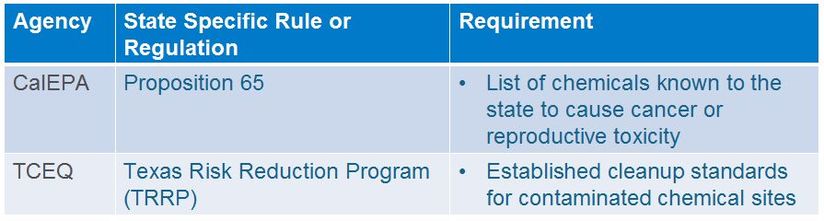
Example agencies that set state toxicology regulations:
- California Environmental Protection Agency (CalEPA)
- Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment (CDPHE)
- Department of Energy & Environment, Government of the District of Columbia (DOEE - DC)
- Nebraska Department of Health & Human Services (Nebraska DHHS)
- New York State Department of Health (NYSDOH)
- Texas Commission on Environmental Quality (TCEQ )
The goal of state agencies is the same as federal agencies, protect people and the environment from health effects associated with chemical exposures.
States have differing regulatory toxicology requirements and focuses. Reasons for the differences could be due to: state history, geography, culture, population size and diversity, major industries, etc…
Examples of state regulatory toxicology as it concerns chemicals in air:
- Texas
- California
Example state toxicology regulations and the requirement that must be followed:
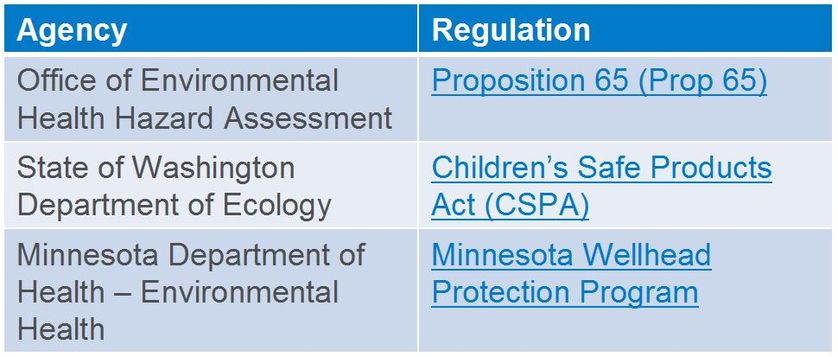
Example agencies that set state toxicology regulations
- CalEPA Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment (OEHHA)
- State of Washington Department of Ecology
- Minnesota Department of Health (MDH) – Environmental Health
An example of a State Regulatory Agency is the CalEPA Office of Environmental Health Hazard Assessment (OEHHA)
- Provides requirements and guidance for the California Proposition 65 Safe Drinking Water and Toxic Enforcement Act of 1986 (Proposition 65)
Proposition 65
- Purpose:
- Enable consumers to make informed decisions regarding chemical exposures.
- Why?
- Established to protect California citizens from chemicals known to the state to cause cancer, birth defects, or other reproductive harms.
- Scope:
- Addresses chemical exposures to the citizens of California that may occur through consumer products, workplace exposures, and exposures occurring via the environment.
|
Basics
|
Proposition 65 upcoming changes…
- The regulation has undergone revisions, New Proposition 65 Warnings, that will now require companies to add a symbol and change the phrasing of the warning. For example: “WARNING: This product can expose you to chemicals including arsenic, which is known to the State of California to cause cancer. For more information, go to www.P65Warnings.ca.gov.”
Topic 5: Key Points
In this section, we explored the following main points:
Two example outcomes of the FSTRAC’s workgroup
Effects Screening Levels (ESLs)
Reference Exposure Levels (RELs)
Texas Risk Reduction Program rule
In this section, we explored the following main points:
- What is State Regulatory Toxicology?
- An example of how federal and state agencies work together
Two example outcomes of the FSTRAC’s workgroup
- Example of State Agencies
- Highlight two state specific guidance and rules as it concerns chemicals in air
Effects Screening Levels (ESLs)
Reference Exposure Levels (RELs)
- Rules
Texas Risk Reduction Program rule