Subtopic 4.1: Introduction
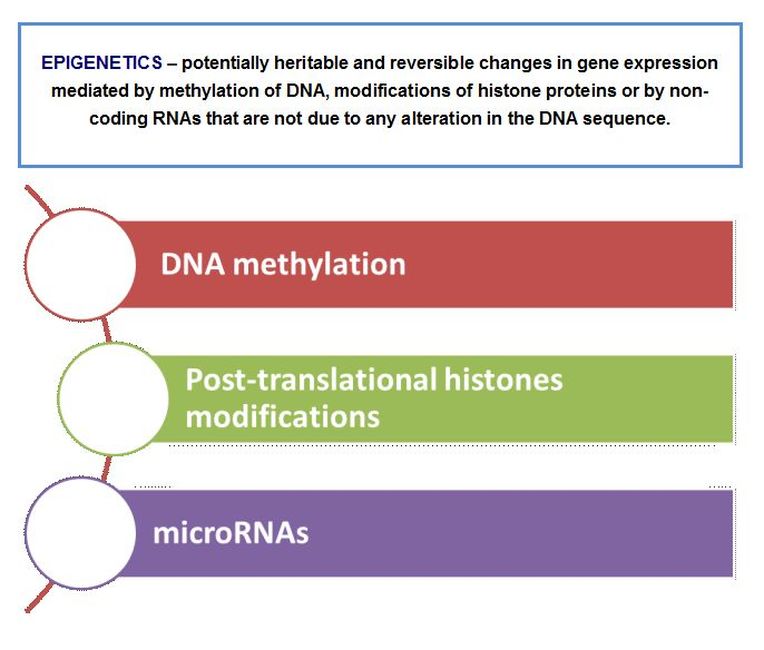
Epigenetics is defined as potentially heritable and reversible and changes in gene expression mediated by methylation of DNA, modifications of histone proteins or by non-coding RNAs that are not due to any alteration in the DNA sequence. These processes singularly or jointly affect transcript stability, DNA folding, nucleosome positioning, chromatin compaction, and ultimately nuclear organization. They determine whether a gene is silenced or activated and when and where this occurs.
Epigenetic change is a regular and natural occurrence, essential for normal cell development, but can also be influenced by several factors including age, the environment/lifestyle, and disease state.
Epigenetic change is a regular and natural occurrence, essential for normal cell development, but can also be influenced by several factors including age, the environment/lifestyle, and disease state.