Subtopic 1.6: RNA
|
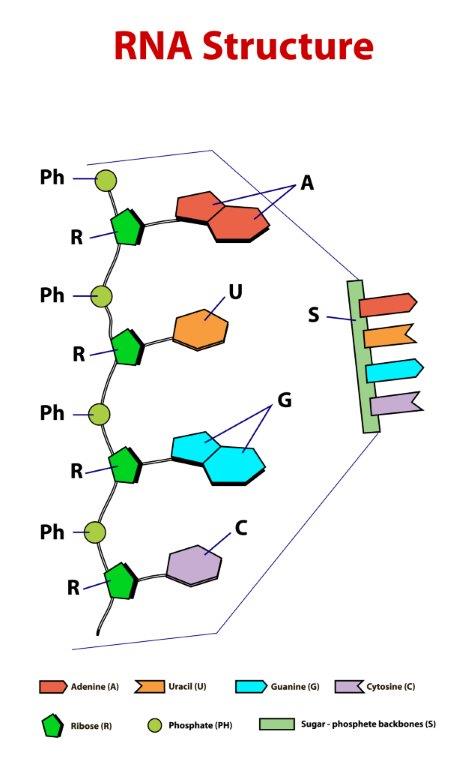
RNA stands for ribonucleic acid. RNA molecules are single strands. RNA components:
RNA molecules often form secondary (2°) structures and may interact with DNA, other RNA molecules, and proteins. These interactions help to define the particular function of each type of RNA. Types of RNA molecules and functions:
|
|
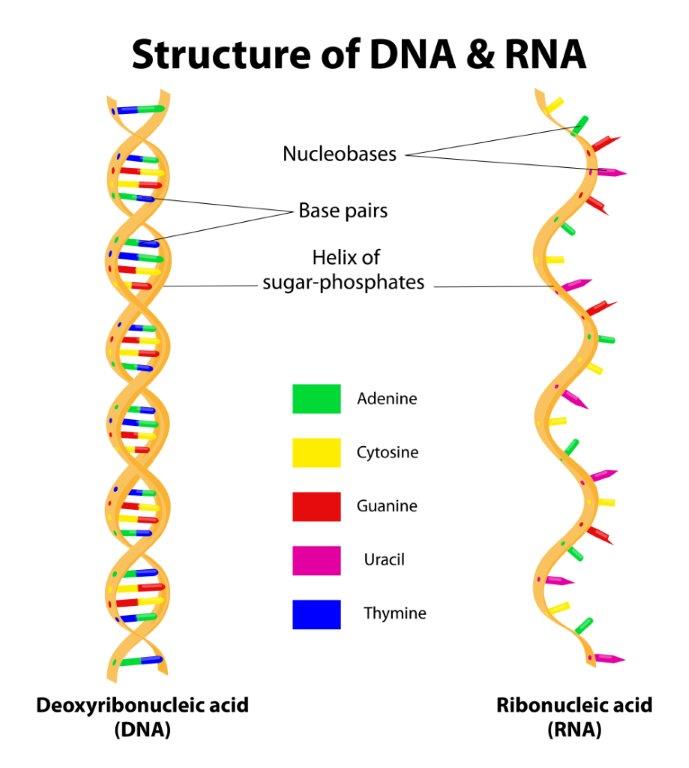
The basic structure of DNA and RNA are similar, however with 3 main differences: 1. Three of the nitrogenous bases are the same in the DNA and RNA: adenine, cytosine, and guanine. The fourth base for DNA is thymine while for RNA is uracil. 2. The DNA molecule is usually double stranded and most cellular RNA molecules are single stranded. 3. In the DNA molecule the sugar is deoxyribose and in the RNA molecule the sugar is ribose |