Dermal Route
In contrast to the thin membranes of the respiratory alveoli and the gastrointestinal villi, the skin is a complex, multilayer tissue. It is relatively impermeable to most ions and aqueous solutions, and serves as a barrier to most xenobiotics.
|
Did you know? Dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) has been used in research, human and veterinary medicine, and as a solvent. After applying to the skin, some people can quickly detect a garlic taste as the DMSO is absorbed and enters the body. DMSO also increases the rate of absorption of some other compounds through the skin. For transdermal drug delivery (TDD), the big challenge is the barrier property of skin, especially the stratum corneum (SC). Different methods have been developed to enhance the penetration of drugs through the skin, with the most popular approach being the use of penetration enhancers (PEs), including natural terpenes. Terpenes, a large and diverse class of organic compounds produced by a variety of plants, are a very safe and effective class of PEs. Limonene is one example of a terpene used as a penetration enhancer. The main mechanism for the penetration enhancing action of terpenes is the interaction with SC intercellular lipids. The key factor affecting the enhancement is the lipophilicity of the terpenes and the drug molecules. |
Figure 1. Nicotine patch
(Image Source: iStock Photos, ©) |
Entry of Toxicants via Skin
Some notable toxicants can gain entry into the body following skin contamination. For example:
Some notable toxicants can gain entry into the body following skin contamination. For example:
- Certain commonly used organophosphate pesticides have poisoned agricultural workers following dermal exposure.
- The neurological warfare agent, sarin, readily passes through the skin and can produce quick death to exposed persons.
- Several industrial solvents can cause systemic toxicity by penetrating the skin. For example:
- Carbon tetrachloride enters the skin and causes liver injury.
- Hexane can pass through the skin and cause nerve damage.
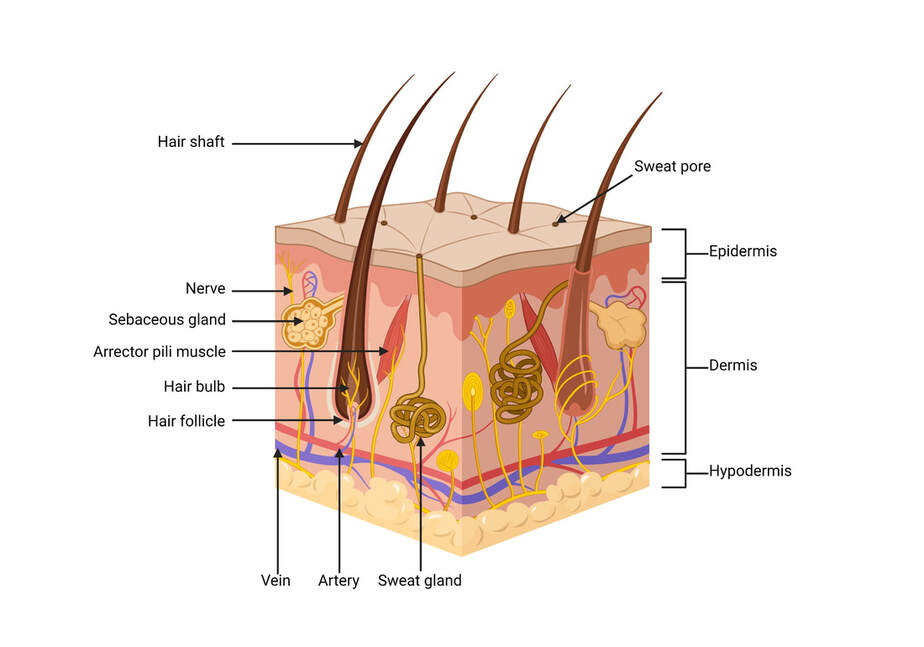
- Epidermis
- Dermis
- Subcutaneous tissue
Figure 2. Layers of the skin
(Image Source: iStock Photos, ©)
(Image Source: iStock Photos, ©)
Epidermis and Stratum Corneum
The epidermis (and particularly the stratum corneum) is the only layer that is important in regulating the penetration of a skin contaminant. It consists of an outer layer of cells, packed with keratin, known as the stratum corneum layer. The stratum corneum is devoid of blood vessels. The cell walls of the keratinized cells are apparently double in thickness due to the presence of the keratin, which is chemically resistant and an impenetrable material. The blood vessels are usually about 100 μM from the skin surface. To enter a blood vessel, an agent must pass through several layers of cells that are generally resistant to penetration by chemicals.
Factors Influencing Penetration of the Stratum Corneum
Thickness
The thickness of the stratum corneum varies greatly with regions of the body. The stratum corneum of the palms and soles is very thick (400-600 μM) whereas that of the arms, back, legs, and abdomen is much thinner (8-15 μM). The stratum corneum of the axillary (underarm) and inguinal (groin) regions is the thinnest with the scrotum especially thin. As expected, the ability of toxicants to penetrate that stratum corneum inversely relates to the thickness of the epidermis.
Damage
Any process that removes or damages the stratum corneum can enhance penetration of a xenobiotic. Abrasion, scratching, or cuts to the skin will make it more penetrable. Some acids, alkalis, and corrosives can injure the stratum corneum and make it easier for agents to penetrate this layer. The most prevalent skin conditions that enhance dermal absorption are skin burns and dermatitis.
Passive Diffusion
Toxicants move across the stratum corneum by passive diffusion. There are no known active transport mechanisms functioning within the epidermis. Polar and nonpolar toxicants diffuse through the stratum corneum by different mechanisms:
Water
Water plays an important role in dermal absorption. Normally, the stratum corneum is partially hydrated (approximately 7% by weight). Penetration of polar substances is about 10 times more effective than when the skin is completely dry. Additional hydration on the skin's surface increases penetration by 3–5 times, which further increases the ability of a polar compound to penetrate the epidermis.
Species
Skin penetration can vary by species which can influence the selection of species used for safety testing. Penetration of chemicals through the skin of the monkey, pig, and guinea pig is often similar to that of humans. The skin of the rat and rabbit is generally more permeable whereas the skin of the cat is generally less permeable. For practical reasons and to assure adequate safety, the rat and rabbit have been used for dermal toxicity safety tests.
Other Sites of Dermal Absorption
In addition to the stratum corneum, small amounts of chemicals may be absorbed through the sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and hair follicles. However, since these structures represent only a very small percentage of the skin's total surface area, they are not ordinarily viewed as important contributors to dermal absorption.
Dermis and Subcutaneous Tissue
Once a substance penetrates through the stratum corneum, it enters lower layers of the epidermis, the dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. These layers are far less resistant to further diffusion. They contain a porous, nonselective aqueous diffusion medium which can be penetrated by simple diffusion. Most toxicants that have passed through the stratum corneum can now readily move through the remainder of the skin and enter the circulatory system via the large numbers of venous and lymphatic capillaries in the dermis.
Semivolatile Organic Compounts (SVOCs)
Exposure to semivolatile organic compounds (SVOCs) via the dermal route can occur. The amount of SVOCs absorbed via air-to-skin uptake has been estimated to be comparable to or larger than the amount taken in via inhalation for many SVOCs encountered indoors, including:
Human exposure to indoor SVOCs through the dermal pathway has often been underestimated and not considered in exposure assessments. However, exposure scientists, risk assessors, and public health officials are increasingly aware of and interested in the health impacts of dermal exposure. Further, experts seek to understand how health consequences can vary by the exposure pathway. For example, an SVOC that enters the blood through the skin does not encounter the same detoxification pathways that it would encounter when ingested and processed by the stomach, intestines, and liver before entering the blood; its direct entry into the blood can make it potentially more toxic.
The epidermis (and particularly the stratum corneum) is the only layer that is important in regulating the penetration of a skin contaminant. It consists of an outer layer of cells, packed with keratin, known as the stratum corneum layer. The stratum corneum is devoid of blood vessels. The cell walls of the keratinized cells are apparently double in thickness due to the presence of the keratin, which is chemically resistant and an impenetrable material. The blood vessels are usually about 100 μM from the skin surface. To enter a blood vessel, an agent must pass through several layers of cells that are generally resistant to penetration by chemicals.
Factors Influencing Penetration of the Stratum Corneum
Thickness
The thickness of the stratum corneum varies greatly with regions of the body. The stratum corneum of the palms and soles is very thick (400-600 μM) whereas that of the arms, back, legs, and abdomen is much thinner (8-15 μM). The stratum corneum of the axillary (underarm) and inguinal (groin) regions is the thinnest with the scrotum especially thin. As expected, the ability of toxicants to penetrate that stratum corneum inversely relates to the thickness of the epidermis.
Damage
Any process that removes or damages the stratum corneum can enhance penetration of a xenobiotic. Abrasion, scratching, or cuts to the skin will make it more penetrable. Some acids, alkalis, and corrosives can injure the stratum corneum and make it easier for agents to penetrate this layer. The most prevalent skin conditions that enhance dermal absorption are skin burns and dermatitis.
Passive Diffusion
Toxicants move across the stratum corneum by passive diffusion. There are no known active transport mechanisms functioning within the epidermis. Polar and nonpolar toxicants diffuse through the stratum corneum by different mechanisms:
- Polar compounds, which are water soluble, appear to diffuse through the outer surface of the hydrated keratinized layer.
- Nonpolar compounds, which are lipid soluble, dissolve in and diffuse through the lipid material between the keratin filaments.
Water
Water plays an important role in dermal absorption. Normally, the stratum corneum is partially hydrated (approximately 7% by weight). Penetration of polar substances is about 10 times more effective than when the skin is completely dry. Additional hydration on the skin's surface increases penetration by 3–5 times, which further increases the ability of a polar compound to penetrate the epidermis.
Species
Skin penetration can vary by species which can influence the selection of species used for safety testing. Penetration of chemicals through the skin of the monkey, pig, and guinea pig is often similar to that of humans. The skin of the rat and rabbit is generally more permeable whereas the skin of the cat is generally less permeable. For practical reasons and to assure adequate safety, the rat and rabbit have been used for dermal toxicity safety tests.
Other Sites of Dermal Absorption
In addition to the stratum corneum, small amounts of chemicals may be absorbed through the sweat glands, sebaceous glands, and hair follicles. However, since these structures represent only a very small percentage of the skin's total surface area, they are not ordinarily viewed as important contributors to dermal absorption.
Dermis and Subcutaneous Tissue
Once a substance penetrates through the stratum corneum, it enters lower layers of the epidermis, the dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. These layers are far less resistant to further diffusion. They contain a porous, nonselective aqueous diffusion medium which can be penetrated by simple diffusion. Most toxicants that have passed through the stratum corneum can now readily move through the remainder of the skin and enter the circulatory system via the large numbers of venous and lymphatic capillaries in the dermis.
Semivolatile Organic Compounts (SVOCs)
Exposure to semivolatile organic compounds (SVOCs) via the dermal route can occur. The amount of SVOCs absorbed via air-to-skin uptake has been estimated to be comparable to or larger than the amount taken in via inhalation for many SVOCs encountered indoors, including:
- Butylated hydroxytoluene (BHT)
- Chlordane
- Chlorpyrifos
- Diethyl phthalate
- Nicotine (in free-base form)
- Other chemicals
Human exposure to indoor SVOCs through the dermal pathway has often been underestimated and not considered in exposure assessments. However, exposure scientists, risk assessors, and public health officials are increasingly aware of and interested in the health impacts of dermal exposure. Further, experts seek to understand how health consequences can vary by the exposure pathway. For example, an SVOC that enters the blood through the skin does not encounter the same detoxification pathways that it would encounter when ingested and processed by the stomach, intestines, and liver before entering the blood; its direct entry into the blood can make it potentially more toxic.
Figure 3. Examples of SVOCs from consumer goods
(Image Source: Adapted from iStock Photos, ©)
(Image Source: Adapted from iStock Photos, ©)
Knowledge Check (Solutions on next page)
1) The main barrier to dermal absorption is the:
a) Stratum corneum
b) Dermis
c) Subcutaneous tissue
2) The two primary factors that can increase dermal penetration are:
a) Neutralizing pH and aerosolizing
b) Increasing hydration and disruption of the stratum corneum
c) Dehydrating a substance and increasing particle size